|
Overview
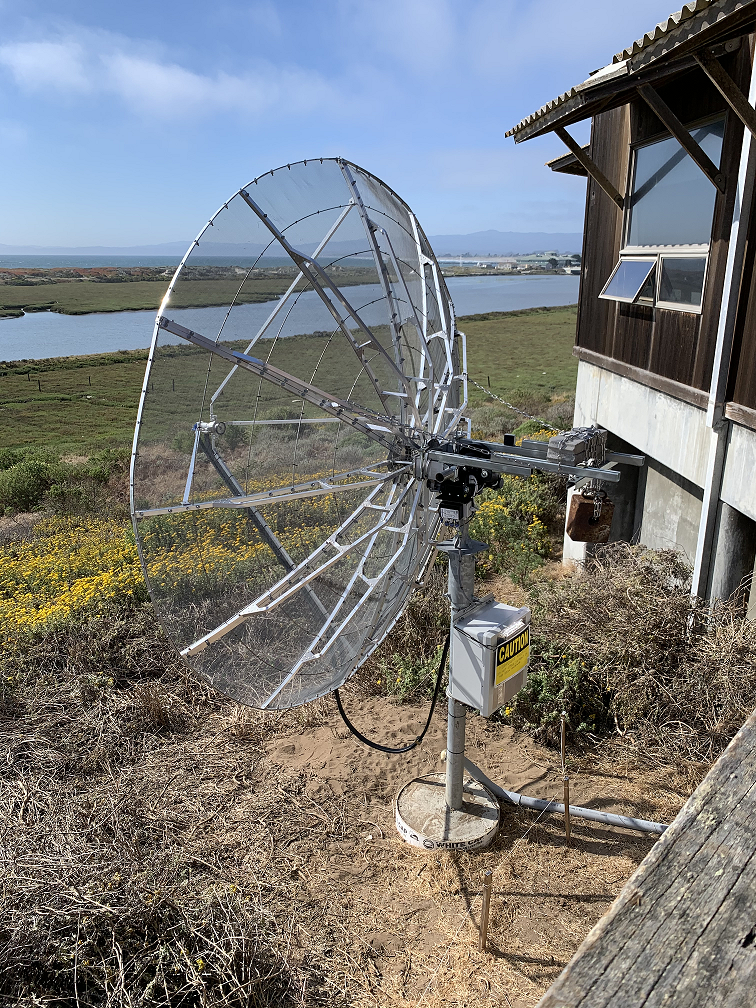
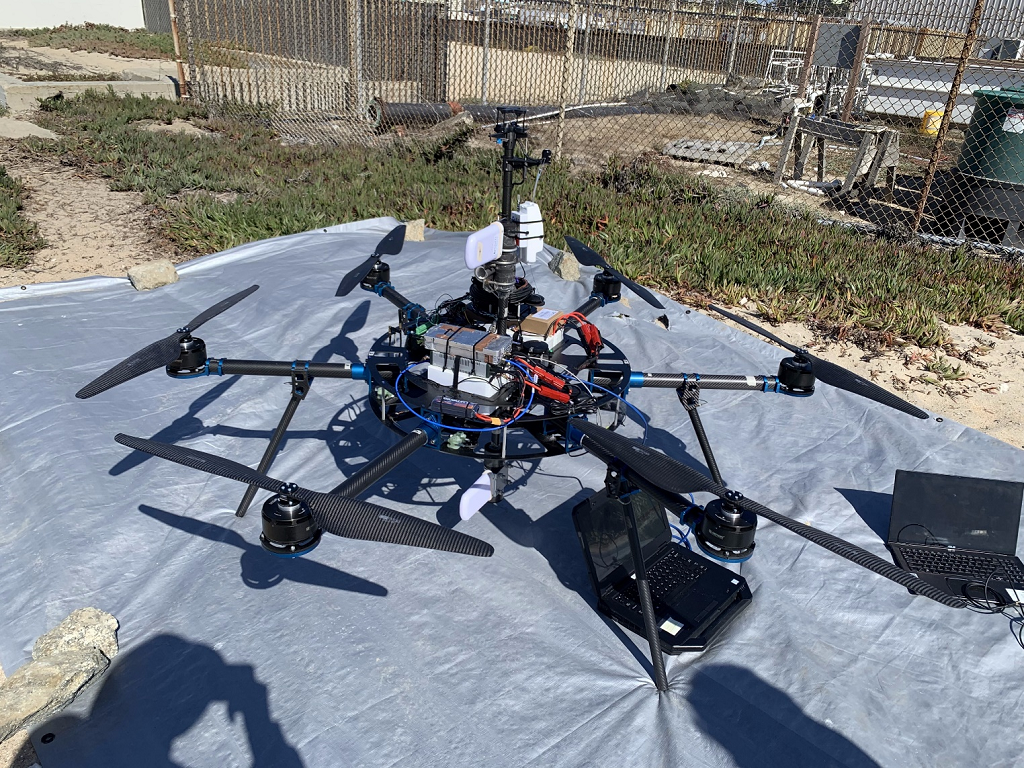
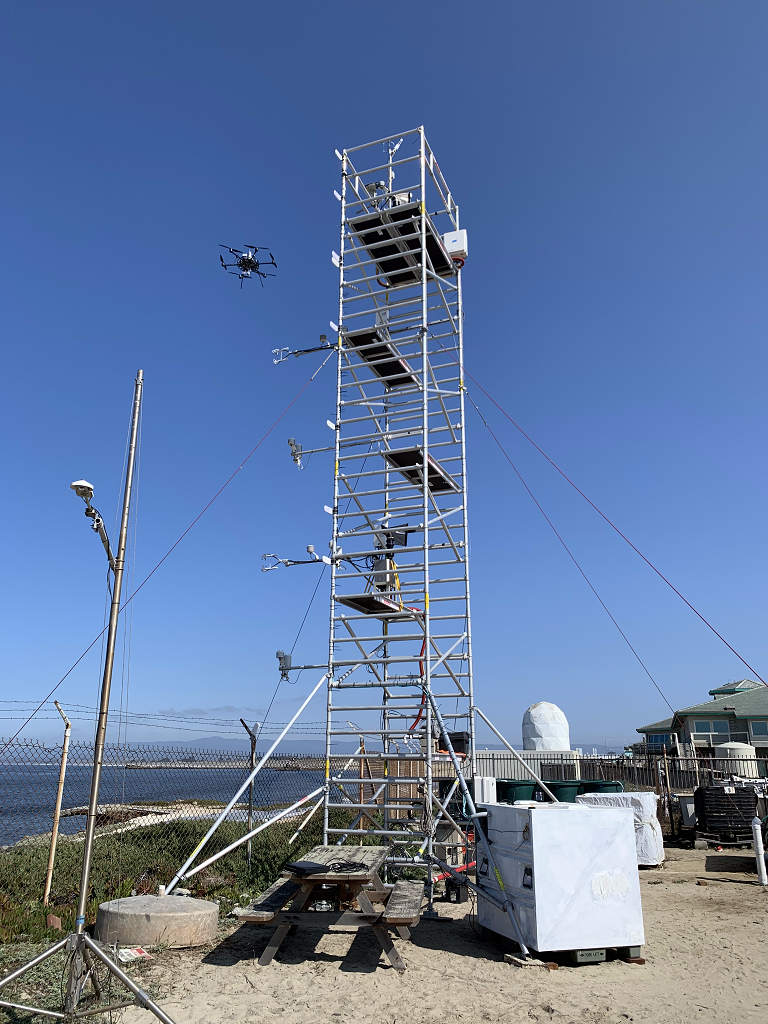
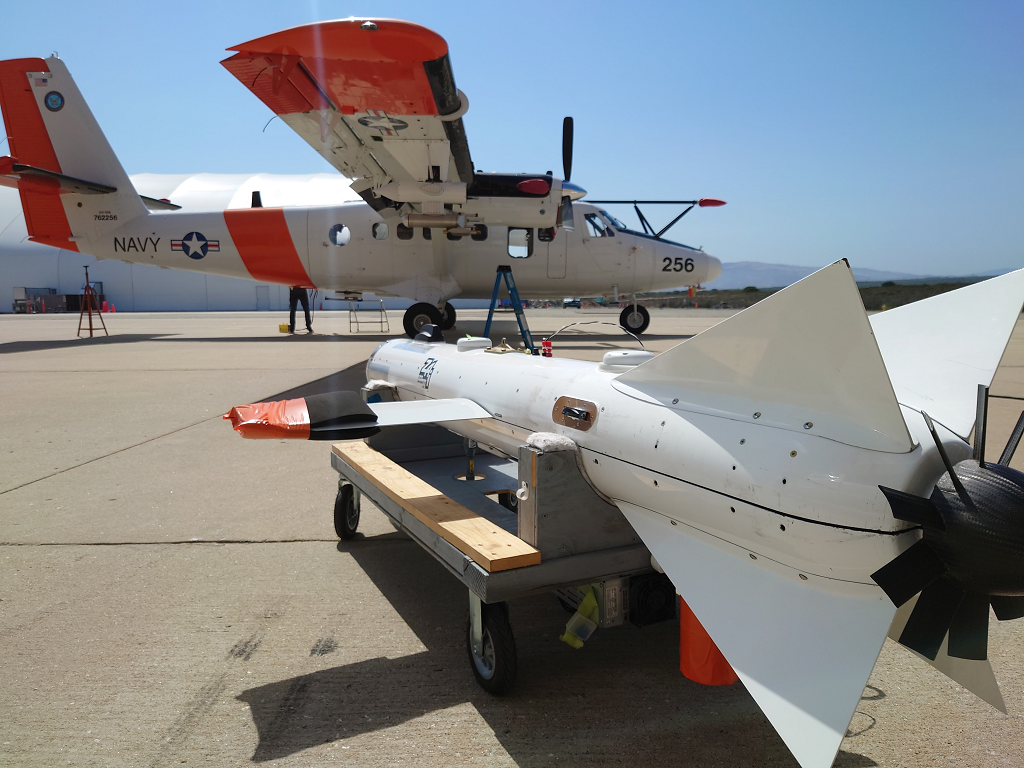
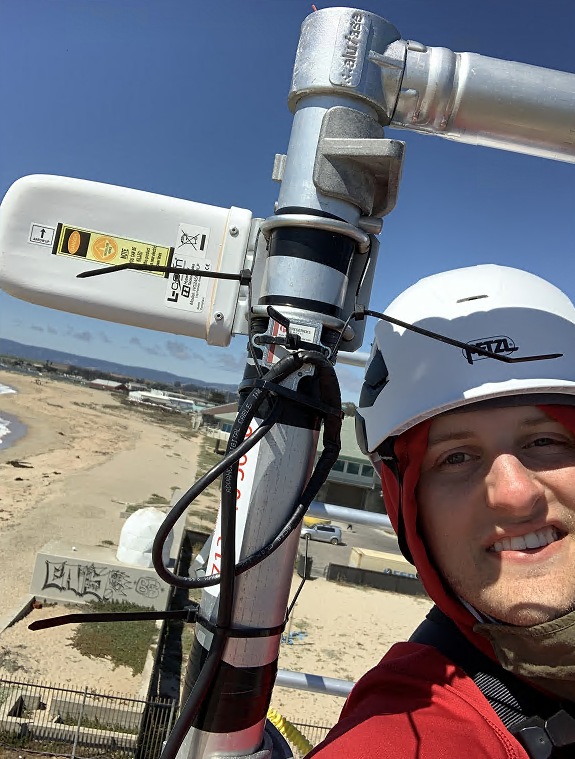
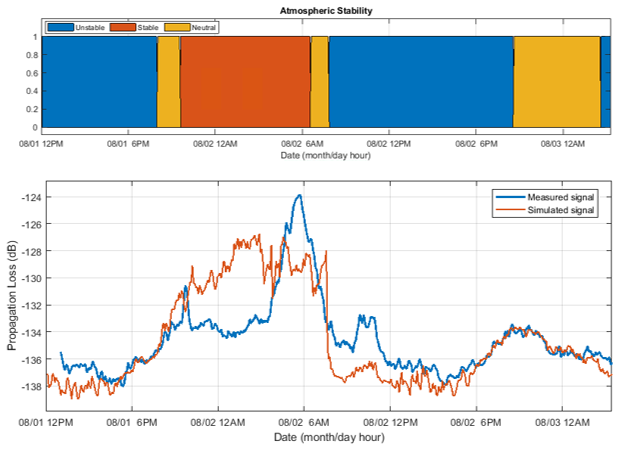
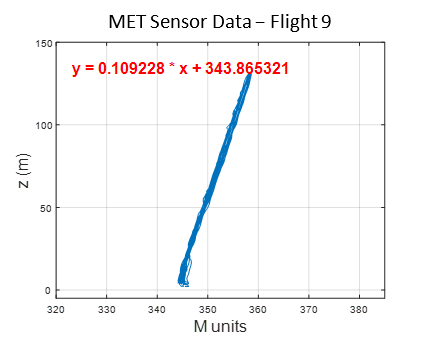
In the marine atmospheric boundary layer propagating electromagnetic signals are effected non-intuitively, especially at coastal boundaries. The team at The Ohio State University has deployed both one-way RF links and high power radar to make observations of the coastal metrology in the electromagnetic domain. Coupled with metrological measurements by other groups in the CLASI campaign and numerical electromagnetic models, the RF measurements will hopefully be used to improve communication and radar systems operating in this environment. The Ohio State University team has deployed three specific systems; a drone-mounted receiver payload which directly measures a large, continuous height profile of the signal power, a phase coherent vertical array for signal power measurement and angle of arrival estimation, and a high power radar system which measures reflections from the sea surface to infer the air refractivity along the two-way propagation path. Drone Receiver System Utilizing an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), The Ohio State University team works to support the CLASI objectives by sampling vertical electromagnetic (EM) signal in the coastal atmospheric boundary layer. These profiles of propagation loss vs altitude are compared using the parabolic wave equation and simulated for different slope values of modified refractivity. The goal is to understand the effect of the environment on the EM and better improve our ability to predict the MET using the EM data. The electromagnetic signal is transmitted continuously from atop three ASIS buoys moored in Monterey Bay. The buoys are moored at different distances from the shore, giving three different propagation characteristics through the MABL. Coherent Vertical Array System The coherent vertical array (CoVA) is a set of RF receivers arranged to measure one-way RF signals propagated from moored ASIS buoys through the marine atmospheric boundary layer (MABL). In previous experiments, the RF signal power at each element has been measured, creating a propagation loss profile with respect to height. CoVA utilizes phase synchronized off the shelf (OTS) software defined radios (SDR) to precisely measure RF signal waveforms such that the phase at each element is known in addition to the signal power. This additional information improves metrological parameter estimation algorithms and allows for angle of arrival (AoA) estimation of the propagated signal, a novel feature for MABL RF remote sensing equipment. CoVA shares use of the electromagnetic signal transmitted from the ASIS buoys with the drone. In addition, a transmitter is mounted to a controlled towed vehicle (CTV) carried by an aircraft. During flight operations, the CTV is flown in a pattern around the bay, causing the transmitted signal on board to undergo various propagation paths through the MABL to the receiver systems. This gives much greater sampling of the MABL during flight operations. Radar System The radar system is an OTS Koden MDS63R marine radar modified to measure Refractivity-from-Clutter (RFC) from the sea surface. The EM radar pulse scatters as it strikes the sea surface and the returning signal power "clutter" infers the atmospheric refractivity profile. The Ohio State University Team |